|
|
|
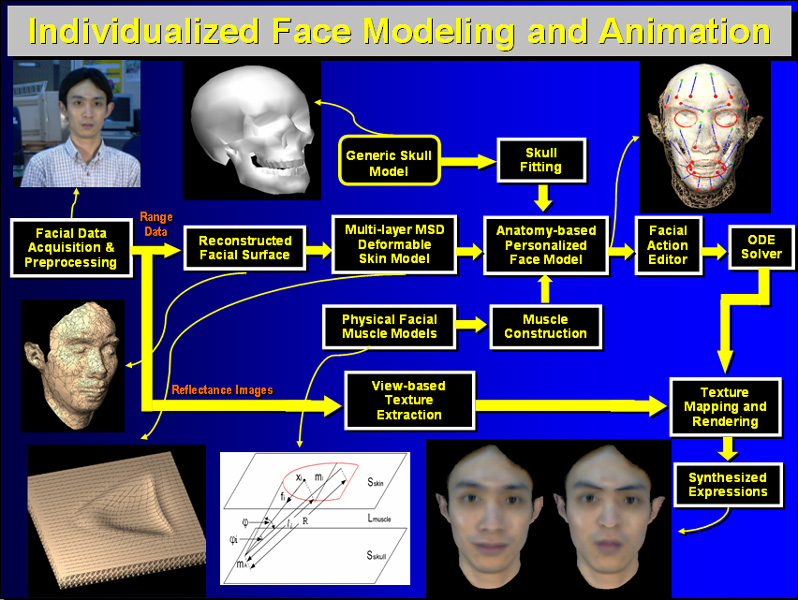
System overview
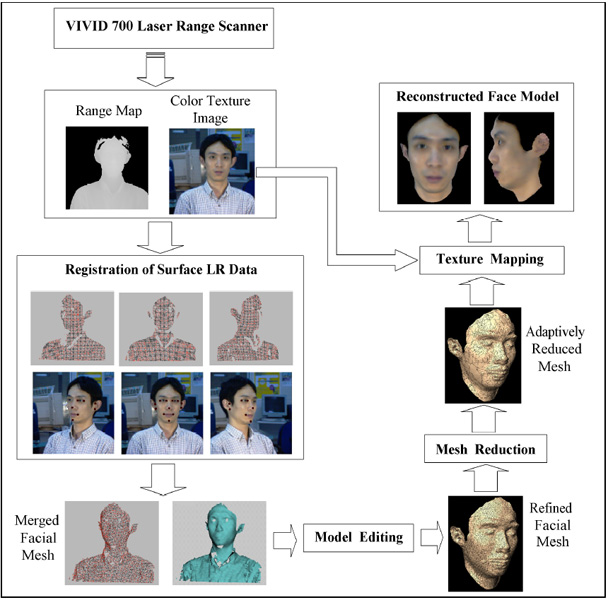
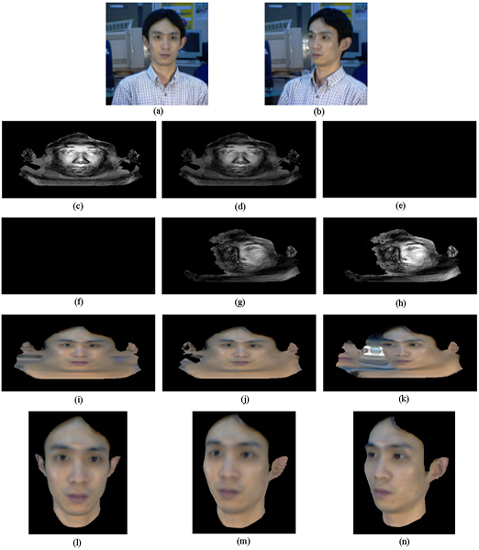
Flow diagram for face geometry reconstruction from range scans
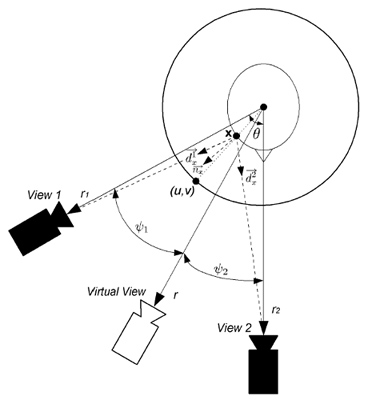
View-dependent texture blending and mapping
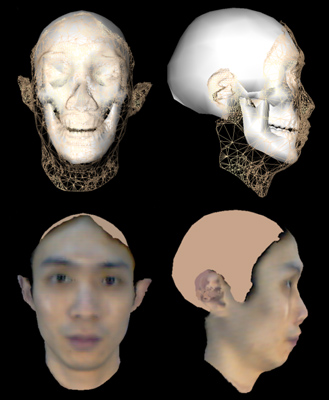
Modeling anatomical structure
A muscle mapping approach for efficient facial muscle construction

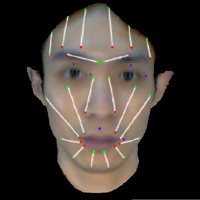



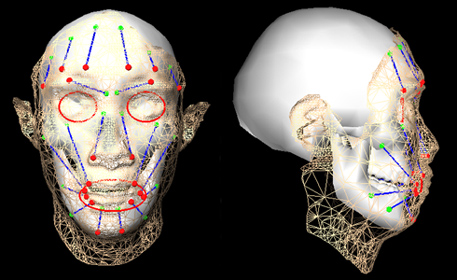
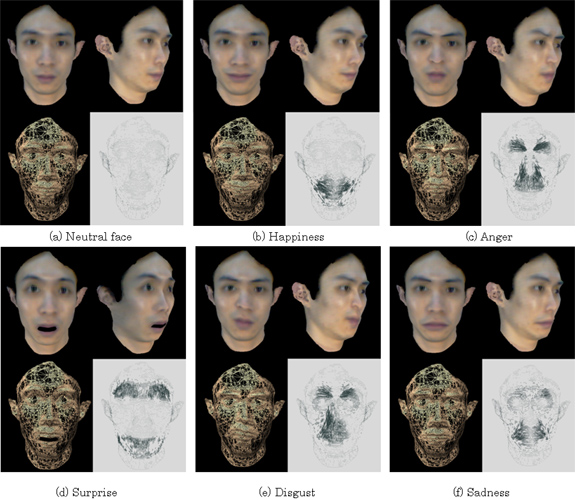
Facial animation






Copyright 2005-2013, Yu
Zhang.
This material may not be published, modified or otherwise
redistributed in whole or part without prior approval.